Dental Service – Dental Implant
What is Involved When Placing Implants?
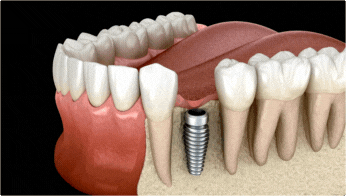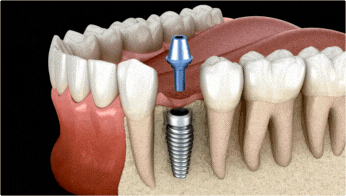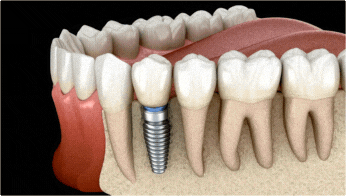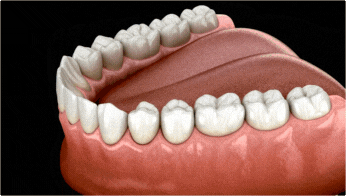
Initially, surgery is performed to place the implant body. It takes up to six months for the bone to grow around the implant body so it firmly holds in place. A second visit is then required to place an abutment on the implant body. In some cases, this requires additional surgery.
After the abutment is in place, an impression is taken so that restorative teeth (such as crowns) can be made to fit the abutment. After the restorative teeth are constructed, they will be placed and cemented on the abutment. Because several fittings may be required before cementing, this step can take one or two months to complete.
Implant surgery can be done with local anesthetic or IV sedation. Usually, pain medications and antibiotics (when necessary) are prescribed. Your dentist will give you careful instructions on post-operative diet and oral hygiene.
Are Implants Right For Me?
If you are considering implants, a thorough evaluation by a qualified surgeon will be scheduled. The evaluation will determine your candidacy for implant placement. This evaluation includes a clinical examination and a complete dental and medical history to gather information about any relevant conditions that you have (such as diabetes, heart problems or any condition that interferes with normal healing). Be sure to tell the dentist about any allergies or any medications that you take (prescribed and over-the-counter). If necessary, the dentist may request a consultation with a physician.
During the examination, the dentist will check the condition of your mouth, the supporting jaw bone and the way your upper and lower teeth fit together. The dentist may gather additional information by taking X-rays and by making models of your teeth. This information will help your dentist determine if you are a good candidate for an implant and decide which implant to use and where to place it.
What Materials Are Used?
Replacement teeth are made of porcelain, metal or polymer resin (the same materials as those used for conventional crowns, bridges and dentures). The implant body and abutment are made from a number of synthetic materials. Titanium is a favored metal for many implants since it is very compatible with bone and other tissues.
